- Contents
- Index
- Introduction to R-Studio
-
Data Recovery Using R-Studio
- Basic File Recovery
- Advanced Data Recovery
- Mass File Recovery
-
Volume Sets and RAIDs
- Volume Sets, Stripe Sets, and Mirrors
- Basic RAID 4 and RAID 5 Operations
- Working with RAID6 (Double Xor) Presets
- Working with RAID 6 Presets
- Working with RAIDs with Parity Delays
- Working with Advanced RAID Layouts
- Nested and Non-Standard RAID Levels
- Finding RAID Parameters
- Checking RAID Consistency
- Syntax of a Description File for RAID Configurations
- Description Files for RAID Configurations
- Various Disk and Volume Managers
- Data Recovery over Network
-
R-Studio Technician/T80+
- USB Activation
- Portable version
- Show Files (Advanced)
- Multitasking
- Additional Recovery Options
- Mounting Virtual Objects in the System as Virtual Drives
- Opening Virtual Disks from the Files Panel
- Hidden Devices
- File Information
- Symbolic Link Processing
- Custom Recovery Lists
- Drive Copy Wizard
- File Maps
- I/O Monitor and Sector Map Files
- Runtime Imaging
- Multi-pass Imaging
- Reverse RAIDs
- Working with Third-Party Hardware
- Forensic Mode
- Text/hexadecimal Editor
- Technical Information and Troubleshooting
- R-Studio Emergency
- R-Studio Agent Emergency
© 2026 R-Tools Technology Inc.
All rights reserved.
Multi-pass Imaging
Multi-pass imaging is a process of image creation through several passes (phases). Each phase reads data from different areas of a hard drive, starting from areas with good sectors then going to slow sector areas and finishes with bad sector areas. This approach maximizes the amount of data that can be recovered from a failing drive and reduces it chances to fail during this process.
Phase 1. Copying most good data from the drive
In this phase, R‑Studio reads data from drive by sector blocks, or groups of consecutive drive sectors read in one go. The phase is performed in several steps.
Step 1. R‑Studio reads data from the drive until it runs into a block with bad or slow sector(s). Then it drops that block and jumps to another area until it finds a block with no bad or slow sectors. Then it continues reading data until it runs into another bad or slow block, and the process repeats. When this step is finished, most good data from the hard drive has been read, and R‑Studio has detected the front blocks (edges) of bad and slow sector areas.
Step 2. R‑Studio finds the rear edges of bad sector areas. It reads the skipped area from its rear end backwards until it runs into a block with a bad sector. Then R‑Studio jumps to another bad sector area and the process is going on until all bad sector areas have been processed. When this step is finished, some good data from the hard drive has been read, and R‑Studio has detected the rear edges of bad sector areas.
Step 3. R‑Studio reads data from slow sector areas. It does that much the same way as for bad sector areas. When this step is finished, good data from slow sectors on the hard drive has been read, and R‑Studio has detected the rear edges of slow sector areas.
Step 4. R‑Studio finds the rear edges of bad sector areas in slow sector areas. When this step is finished, some new good data from slow sectors on the hard drive has been read, and R‑Studio has detected the rear edges of all bad sectors within slow sector areas.
Step 5. R‑Studio tries to read all skipped sector blocks. This is done without skipping bad sector blocks and checking read speed against minimum I/O rate.
When Phase 1 is completed, R‑Studio has read most of readable data and detected front and rear edges of all bad sector areas.
R‑Studio tries to read the rest of data in the next phases, and does that sector by sector (rather than blocks).
Phase 2. Trimming
R‑Studio detects the front and rear sectors of bad sector areas. When this step is finished, some new good data from bad sector areas has been read, and R‑Studio has detected the front and rear sectors of all bad sector areas.
Phase 3. Scraping
R‑Studio tries to read data from bad sector areas sector by sector.
Phase 4. Retrying (mostly optional)
R‑Studio tries to read data from bad sectors through several attempts.
You may read more about this process in our article Multi-pass imaging in R-Studio
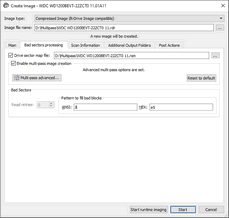
To create an image through multi-pass imaging,
| 1 | Select an object in the R‑Studio 's Drives panel and click the Create Image button |
 Other ways to create the image
Other ways to create the image
|
• Select the object and select Create Image on the Drive menu or • Right-click the selected object and select Create Image File on the shortcut menu |
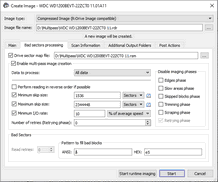
| 2 | Specify image options, a file name, and destination for the image on the Create Image dialog box and click the OK button |
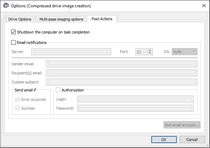
![]() Bad sectors processing options
Bad sectors processing options
|
Some options can be changed even during the process of image creation. |
|
|
Image filename |
Specifies the name and path for the image file |
|
Image type: |
Compressed image (R-Drive Image compatible): If this option is selected, R‑Studio will create an image file which can be compressed, split into several parts, and password-protected. This image file is fully compatible with the images created by R-Drive Image , but incompatible with very old versions of R‑Studio . Byte by byte image to a file: If this option is selected, R‑Studio will create a simple exact copy of the object. Byte to byte image to a physical disk : R‑Studio will create an exact copy of the disk on another hard drive. Data on the target drive will be overwritten. Available in the Corporate, Technician, and T80+ licenses. Some other image formats are also available in the Technician, and T80+ licenses. You may read more about these formats in the Supported Virtual Disk and Disk Image Formats page. |
|
A file with the sector map of the object to image. Optional for the RDI image type, mandatory for the other image types. |
|
|
Enable multi-pass image creation |
Turns multi-pass imaging on and off. |
|
Data to process |
All data : All data on the disk will be imaged. Existing files only (FS bitmap) : Only the disk area occupied by the existing files of the file system will be imaged. If there are more than one partition exist on a hard drive, existing files will be imaged from all partitions. Unused clusters only : Only the unused clusters of the file system will be imaged. If there are more than one partition exist on a hard drive, unused clusters will be imaged from all partitions. Existing files + Unused clusters: First the existing files then the unused clusters will be imaged. 2 image files will be created. Unused clusters + Existing files: First the unused clusters then the existing file s will be imaged. 2 image files will be created. |
|
Perform reading in reverse order if possible |
Switches the direction of all phases/steps to reverse. |
|
Use less strict options for FS metadata |
When this option is selected, the area where FS metadata resides will be treated differently: Block size will be smaller, no skipped blocks, I/O timeout will be increased for devices with support of such features. |
|
Minimum skip size |
Minimum size of drive area to skip when a bad sector is encountered. |
|
Maximum skip size |
Maximum size of drive area to skip when a bad sector is encountered. |
|
Slow I/O rate |
Data read rate from which the block being read will be trated as a slow one. Can be either as % of average speed or in Mb/sec. It can also be turned off. |
|
Number of retries (Retrying phase) |
The number of read attempts in the Retrying phase. |
|
Block size |
The block size to process as a single unit. |
|
Disable imaging phases |
Multi-imaging phases that can be skipped. They can be skipped or added even during image creation |
|
Start runtime imaging |
Click this button to switch to runtime imaging . |
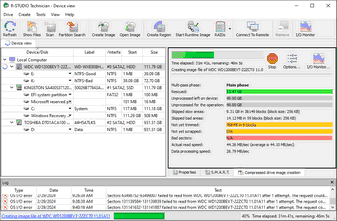
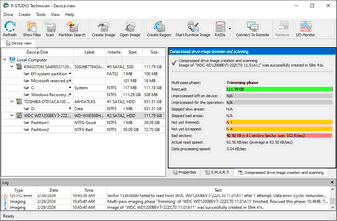
| > | R‑Studio will start creating the image, the Progress showing the progress. |
You may change some operation parameters during image creation. Click the Options button and change them accordingly.
When the imaging is over, R‑Studio will show its results.
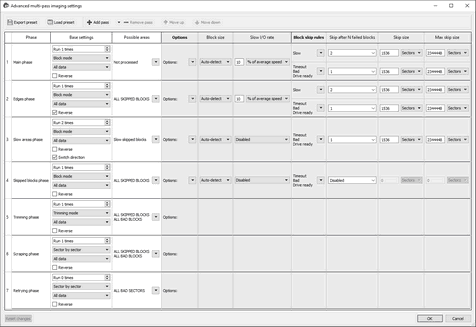
Advanced multi-pass imaging settings window
Note: You should completely understand what you are going to do, or you may severe deteriorate R‑Studio performance or even damage the hard drive being imaged. When in doubt, confine yourself to parameters on the Multi-pass imaging options tab.
The Bad sector processing dialog box spe cifies options for all stages of multi-pass imaging. You can perform more versatile control of these options on the Advanced multi-pass imaging settings window. You may add or delete individual phases and steps, change their order, and fine-tune each phase and step separately.
Depending on the phase/step, these options are different. Some of them are described in the Bad sectors processing options tab, some are self-evident, and some are described in the table below.
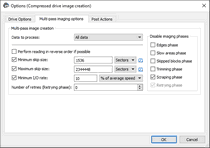
![]() Advanced bad sectors processing options
Advanced bad sectors processing options
|
Possible areas |
Specifies the areas to which this phase will be applied . Selecting an area in ALL CAPITALS selects all their subareas . |
|
Options |
You may specify separate options for sectors where FS metadata resides. |
|
Block skip rules Skip after N failed blocks |
Specifies how many times various failed blocks will be encountered to skip them. |
Some additional options may appear when third-part hardware is used.
A particular set of these options can be saved as a preset and loaded back when necessary.
The Bad sector processing tabs will look different when the advanced multi-pass imaging settings have been altered.
- R-Studio Technician: activation using a USB stick
- Data Recovery Guide
- Why R-Studio?
- R-Studio for Forensic and Data Recovery Business
- R-STUDIO Review on TopTenReviews
- File Recovery Specifics for SSD devices
- How to recover data from NVMe devices
- Predicting Success of Common Data Recovery Cases
- Recovery of Overwritten Data
- Emergency File Recovery Using R-Studio Emergency
- RAID Recovery Presentation
- R-Studio: Data recovery from a non-functional computer
- File Recovery from a Computer that Won't Boot
- Clone Disks Before File Recovery
- HD Video Recovery from SD cards
- File Recovery from an Unbootable Mac Computer
- The best way to recover files from a Mac system disk
- Data Recovery from an Encrypted Linux Disk after a System Crash
- Data Recovery from Apple Disk Images (.DMG files)
- File Recovery after Re-installing Windows
- R-Studio: Data Recovery over Network
- How To Use R-Studio Corporate Package
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted NTFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an ReFS disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted exFAT/FAT Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased HFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased APFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted Ext2/3/4FS Disk
- Data Recovery from an XFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Simple NAS
- How to connect virtual RAID and LVM/LDM volumes to the operating system
- Specifics of File Recovery After a Quick Format
- Data Recovery After Partition Manager Crash
- File Recovery vs. File Repair
- Data Recovery from Virtual Machines
- How to Recover Files from a Remote Computer Using R-Studio Standalone License and Its Network Capabilities in Demo Mode
- How to Connect Disks to a Computer
- Emergency Data Recovery over Network
- Data Recovery over the Internet
- Creating a Custom Known File Type for R-Studio
- Finding RAID parameters
- Recovering Partitions on a Damaged Disk
- NAT and Firewall Traversal for Remote Data Recovery
- Data Recovery from an External Disk with a Damaged File System
- File Recovery Basics
- Default Parameters of Software Stripe Sets (RAID 0) in Mac OS X
- Data Recovery from Virtual Hard Disk (VHD/VHDX) Files
- Data Recovery from Various File Container Formats and Encrypted Disks
- Automatic RAID Parameter Detection
- IntelligentScan Data Recovery Technology
- Multi-pass imaging in R-Studio
- Runtime Imaging in R-Studio
- Linear Imaging vs Runtime Imaging vs Multi-Pass Imaging
- USB Stabilizer Tech for unstable USB devices
- Joint work of R-Studio and PC-3000 UDMA hardware
- Joint work of R-Studio and HDDSuperClone
- R-Studio T80+ - A Professional Data Recovery and Forensic Solution for Small Business and Individuals Just for 1 USD/day
- Backup Articles
- R-Drive Image Standalone and Corporate license transferring
- Fixing Windows update error 0x80070643 with R-Drive Image
- Backup with Confidence
- R-Drive Image as a free powerful partition manager
- Computer Recovery and System Restore
- Disk Cloning and Mass System Deployment
- Accessing Individual Files or Folders on a Backed Up Disk Image
- R-Drive Image startup / bootable version
- File Backup for Personal Computers and Laptops of Home and Self-Employed Users
- Creating a Data Consistent, Space Efficient Data Backup Plan for a Small Business Server
- How to Move the Already Installed Windows from an Old HDD to a New SSD Device and Create a Hybrid Data Storage System
- How to Move an Installed Windows to a Larger Disk
- How to Move a BitLocker-Encrypted System Disk to a New Storage Device
- How to backup and restore disks on Linux and Mac computers using R-Drive Image
- R-Drive Image and Virtual Machines
- Undelete Articles
- Get Deleted Files Back
- Free Recovery from SD and Memory cards
- R-Undelete: Video Recovery
- Recovery from an External Device with a Damaged File System
- File recovery from a non-functional computer
- Free File Recovery from an Android Phone Memory Card
- Free Photo and Video File Recovery Tutorial
- Easy file recovery in three steps