-
File Recovery Specifics for SSD and Other Devices Supporting the TRIM/UNMAP command
(TRIM is a SATA command, UNMAP is its SCSI/SAS analog)
For years speed and capacity have been the most challenging parameters for storage devices. At the same time such devices should remain compact and not power-hungry, which is especially important for laptops and portable storage devices. Such devices should also be affordable to home and small business consumers. Electronic industry has come out with a rational solution: it offers solid-state drives (SSD) as ultra fast storage devices and 2.5" SMR hard drives as high-capacity yet compact and low-power-consuming storage devices. Respectively, SSDs are used primarily as system devices, scratch, and temporary storage devices due to their speed, while 2.5" SMR hard drives are used as high-capacity storages. And when both these types are used together, the overall hybrid system becomes very fast and capacious. Our article "How to Move the Already Installed Windows from an Old HDD to a New SSD Device and Create a Hybrid Data Storage System" explains how to create such a system.
Beside a lot of advantages, such devices have some drawbacks, especially when it comes to accidentally deleted or lost files recovery. In this article we will explain why it's so and what to expect when you recover files from a device with the TRIM/UNMAP command.
We'll start our explanations with some basic principles of their operations.
SSD devices
Most modern computers, even very inexpensive ones, have an SSD as their system storage device (and quite often the only one). Such devices are faster, run silently, consume less power, and more resistant to physical shock when compared to conventional hard disk drives.
There are two types of SSD devices which differ in their form factors: with the old 2.5" one (the same as for conventional HDDs) and a new one M.2, which looks similar to a memory plank.
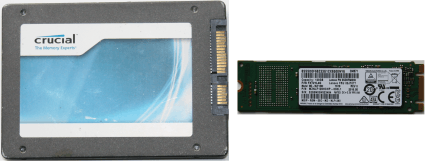
Fig.1. Two form-factors of SSD storage devices: 2.5" (left) and M.2 (right)
Click image to enlarge
Unfortunately, such devices have also some serious drawbacks, with file recovery being one of them.
SSD Basics
When a file is deleted from a mechanical drive, the OS simply marks the disk area occupied by the file as free, but its data is left on the disk untouched until some new file overwrites it. When a data recovery program accesses the untouched area it gets the old data. That is how file recovery works.
An SSD however, must either use its new cells, or first purge the old data in the occupied cells to store the fresh data. Purging old data in SSDs is quite a slow process. That is why file deletion in an SSD works in the following way: when a user, program, or OS itself deletes a file, the OS issues the TRIM command that informs the SSD that the data is no longer needed. The SSD puts the cells the file occupied to a special pool to be purged later. When any program or OS requests data from those cells, the SSD simply returns garbage or zeros.
Moreover, the device constantly shuffles the data across its cells to level their wear, and only the device itself knows where the file data is stored at any given time. The OS has no control over this process, and furthermore, it has no means to know the actual physical location of the data.
This is why data recovery from SSD devices when the TRIM command is used is extremely difficult, and in most cases impossible.
SSDs are solid state storage devices, like other flash memory types (SD cards, memory sticks, and alike), but not all solid state storage devices are SSDs. R-Studio shows whether the flash device supports the TRIM command in the Features field on the S.M.A.R.T. tab.
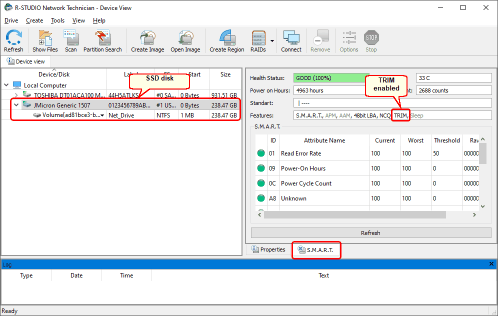
Fig.2.TRIM support in SSD devices
Click image to enlarge
Hard drives with the SMR technology
The SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) technology is used to overcome the main obstacle for increasing capacity in compact hard drive: limitations for storage density. Unlike conventional hard drives which write data in non-overlapping magnetic tracks parallel to each other, SMR drives write data in partially overlapping tracks allowing for higher track density. Such recording resembles roof shingles, hence the name.
This technology indeed increases hard drive capacity, but when data is to be overwritten or deleted, this operation will affect a part of other overlapping tracks with the corresponding data, too. To save the data on the overlapping tracks, it should be written elsewhere, which makes this operation very slow. To accelerate this process, the same principles as in SSD devices and the same command TRIM are used. The effect to data recovery is the same: when any program or OS requests data from deleted files, the hard drive returns zeros or garbage, making data recovery extremely difficult or impossible.
Usually SMR disks bear a special mark on its case.
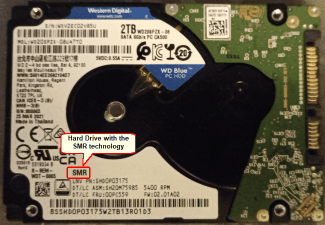
Fig.3.Hard drive with the SMR technology
Click image to enlarge
R-Studio shows whether the hard drive supports the TRIM command in the Features field on the S.M.A.R.T. tab.
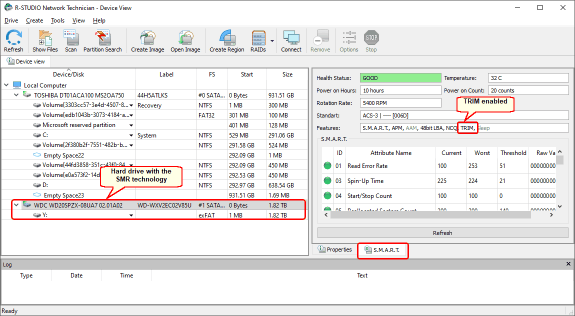
Fig.4.TRIM support in hard drives with the SMR technology
Click image to enlarge
Storage devices, OSs, and file systems that support the TRIM command
TRIM works when all three components support it: a storage device, operating system, and file system on the TRIM-supported device. Almost all modern SSD devices and 2.5" hard drives large than 1 TB support the TRIM command. As for complex volumes consisting of SSDs and SMR hard drives, it depends. Linux LVM2 and Windows software RAIDs support TRIM, whereas software RAIDs in macOS and most hardware RAID controllers don't.
Virtual disks of virtual machines are a little trickier. The fact that a virtual disk is stored on a TRIM-supported devices doesn't mean anything. For the host OS, this disk is a valid file and all disk operations of its virtual machine is read-write operations for that file. Inside the virtual machine with a virtual TRIM-supported disk, it all depends on the virtualization software. Some just simulate the TRIM command and return garbage without any actual changes on the SSD file, while some change file data.
Major OSs and file systems that support the TRIM command:
| TRIM on/off by default | File systems | When TRIM is issued |
| Windows (7 and newer) | ||
| On | NTFS and ReFS (Windows Storage Space only) | Immediately upon deletion |
| macOS (Mac OS X Lion 10.6.8 and newer) | ||
|
On on native Apple SSD devices Off on non-native devices |
APFS and HFS+ | Immediately upon deletion |
| Linux (Kernel 2.6.28 and newer) | ||
| On on most distros, but depends on settings. | Ext4, Btrfs, JFS, XFS, F2FS, NTFS | Depends on distros and settings, usually weekly, but may be immediately upon deletion |
How the TRIM command affects data recovery
Deleted files and formatted disks:
Windows and Mac: Almost always impossible. Even raw file recovery cannot help.
Linux: Possible if done before the TRIM command is issued.
Files lost in slightly damaged file systems (recognized by their native OS):
Every OS is gradually repairing such file systems using the TRIM command to delete garbage, invalid file records, and unnecessary files. Data recovery is possible if done fast and on systems with the TRIM command disabled.
Severely damaged file systems (not recognized by their native OS):
Data recovery is possible because the OS cannot repair them and doesn't delete any data.
How to minimize the negative effect of the TRIM command
Some steps can be made to minimize the negative effect of the TRIM command when the data recovery is possible.
- Disable the TRIM command while recovering data. Don't forget to enable it once file recovery is complete.
Windows:
Press Win + X key key combination.
Windows PowerShell will appear:
Enter "fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify 0/1"
(1 to disable, 0 to enable)
macOS:
In Terminal, enter "sudo trimforce disable"
Enter the administrative password, and answer "Y" to several questions.
The computer will automatically restart with TRIM disabled
To enable TRIM back, enter "sudo trimforce enable".
Linux:
Depends on distros and settings. Consult documentation for the particular installation.
Conclusion
Data recovery from TRIM-supporting devices operating on a major modern OS is mostly impossible for deleted files and formatted devices, and very difficult in other cases, at least when only software solutions are used. Anyone claiming otherwise is either incompetent or willfully deceiving their customers. The exception is a very small number of highly advanced data recovery companies with qualified personnel that in some cases can recover data deleted from an SSD device with the enabled TRIM command. Still, such procedure requires physical access to device's internal components and a lot of manual investigation.
This is why proper and regular data backup is especially important for computers with SSD storage devices. R-Drive Image, created by R-TT Inc., is a powerful and adored software for backing up SSDs and another storage devices. You can download its fully functional version and try it for 30 days with no restrictions.
- R-Studio Technician: activation using a USB stick
- Data Recovery Guide
- Why R-Studio?
- R-Studio for Forensic and Data Recovery Business
- R-STUDIO Review on TopTenReviews
- File Recovery Specifics for SSD devices
- How to recover data from NVMe devices
- Predicting Success of Common Data Recovery Cases
- Recovery of Overwritten Data
- Emergency File Recovery Using R-Studio Emergency
- RAID Recovery Presentation
- R-Studio: Data recovery from a non-functional computer
- File Recovery from a Computer that Won't Boot
- Clone Disks Before File Recovery
- HD Video Recovery from SD cards
- File Recovery from an Unbootable Mac Computer
- The best way to recover files from a Mac system disk
- Data Recovery from an Encrypted Linux Disk after a System Crash
- Data Recovery from Apple Disk Images (.DMG files)
- File Recovery after Re-installing Windows
- R-Studio: Data Recovery over Network
- How To Use R-Studio Corporate Package
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted NTFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an ReFS disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted exFAT/FAT Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased HFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased APFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted Ext2/3/4FS Disk
- Data Recovery from an XFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Simple NAS
- How to connect virtual RAID and LVM/LDM volumes to the operating system
- Specifics of File Recovery After a Quick Format
- Data Recovery After Partition Manager Crash
- File Recovery vs. File Repair
- Data Recovery from Virtual Machines
- How to Recover Files from a Remote Computer Using R-Studio Standalone License and Its Network Capabilities in Demo Mode
- How to Connect Disks to a Computer
- Emergency Data Recovery over Network
- Data Recovery over the Internet
- Creating a Custom Known File Type for R-Studio
- Finding RAID parameters
- Recovering Partitions on a Damaged Disk
- NAT and Firewall Traversal for Remote Data Recovery
- Data Recovery from an External Disk with a Damaged File System
- File Recovery Basics
- Default Parameters of Software Stripe Sets (RAID 0) in Mac OS X
- Data Recovery from Virtual Hard Disk (VHD/VHDX) Files
- Data Recovery from Various File Container Formats and Encrypted Disks
- Automatic RAID Parameter Detection
- IntelligentScan Data Recovery Technology
- Multi-pass imaging in R-Studio
- Runtime Imaging in R-Studio
- Linear Imaging vs Runtime Imaging vs Multi-Pass Imaging
- USB Stabilizer Tech for unstable USB devices
- Joint work of R-Studio and PC-3000 UDMA hardware
- Joint work of R-Studio and HDDSuperClone
- R-Studio T80+ - A Professional Data Recovery and Forensic Solution for Small Business and Individuals Just for 1 USD/day
- Backup Articles
- R-Drive Image Standalone and Corporate license transferring
- Fixing Windows update error 0x80070643 with R-Drive Image
- Backup with Confidence
- R-Drive Image as a free powerful partition manager
- Computer Recovery and System Restore
- Disk Cloning and Mass System Deployment
- Accessing Individual Files or Folders on a Backed Up Disk Image
- R-Drive Image startup / bootable version
- File Backup for Personal Computers and Laptops of Home and Self-Employed Users
- Creating a Data Consistent, Space Efficient Data Backup Plan for a Small Business Server
- How to Move the Already Installed Windows from an Old HDD to a New SSD Device and Create a Hybrid Data Storage System
- How to Move an Installed Windows to a Larger Disk
- How to Move a BitLocker-Encrypted System Disk to a New Storage Device
- How to backup and restore disks on Linux and Mac computers using R-Drive Image
- R-Drive Image and Virtual Machines
- Undelete Articles
- Get Deleted Files Back
- Free Recovery from SD and Memory cards
- R-Undelete: Video Recovery
- Recovery from an External Device with a Damaged File System
- File recovery from a non-functional computer
- Free File Recovery from an Android Phone Memory Card
- Free Photo and Video File Recovery Tutorial
- Easy file recovery in three steps
Rating: 4.8 / 5
R-TT may not be the easiest or most user-friendly solution, but the algorithm used for the renaming saved me THOUSAND of hours of opening ...