- Contents
- Index
- Introduction to R-Studio for Mac
-
Data Recovery Using R-Studio
- Basic File Recovery
- Advanced Data Recovery
- Mass File Recovery
-
Volume Sets and RAIDs
- Volume Sets, Stripe Sets, and Mirrors
- Basic RAID 4 and RAID 5 Operations
- Working with RAID6 Presets
- Working with RAID6 (Double Xor) Presets
- Working with RAIDs with Parity Delays
- Working with Advanced RAID Layouts
- Nested and Non-Standard RAID Levels
- Finding RAID Parameters
- Checking RAID consistency
- Syntax of a Description File for RAID Configurations
- Description Files for RAID Configurations
- Various Disk and Volume Managers
- Data Recovery over Network
-
R-Studio Technician/T80+
- USB Activation (Technician only)
- Show Files (Advanced)
- Multitasking
- Additional Recovery Options
- Connecting Virtual Objects to the System as Virtual Drives
- Opening Virtual Disks from the Files Panel
- Hidden Devices
- Extended File Information
- Symbolic Link Processing
- Custom Recovery Lists
- Drive Copy Wizard
- File Maps
- I/O Monitor and Sector Map Files
- Runtime Imaging
- Multi-pass Imaging
- Reverse RAIDs
- Working with the Third-Party Hardware
- Forensic Mode
- Text/Hexadecimal Editor
- Technical Information and Troubleshooting
- R-Studio Emergency
- R-Studio Agent Emergency
© 2025 R-Tools Technology Inc.
All rights reserved.
Working with RAIDs with Parity Delays
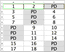
R-Studio allows you to create RAIDs with parity delays (any level that allows that). For example, let us create a RAID 5 the parity delays with the following layout:
• Three disks,
• Delay=16
• Block size: 16 KB
• Offset: 1088 sectors (544 KB)
• Block order: Left Asynchronous (Continuous)
|
|
A |
B |
C |
Delay=16 |
|
1 |
1 |
2 |
PD |
|
|
2 |
3 |
4 |
PD |
|
|
3 |
5 |
6 |
PD |
|
|
4 |
7 |
8 |
PD |
|
|
5 |
9 |
10 |
PD |
|
|
6 |
11 |
12 |
PD |
|
|
7 |
13 |
14 |
PD |
|
|
8 |
15 |
16 |
PD |
|
|
9 |
17 |
18 |
PD |
|
|
10 |
19 |
20 |
PD |
|
|
11 |
21 |
22 |
PD |
|
|
12 |
23 |
24 |
PD |
|
|
13 |
25 |
26 |
PD |
|
|
14 |
27 |
28 |
PD |
|
|
15 |
29 |
30 |
PD |
|
|
16 |
31 |
32 |
PD |
|
|
17 |
33 |
PD |
34 |
Delay=16 |
|
18 |
35 |
PD |
36 |
|
|
19 |
37 |
PD |
38 |
|
|
20 |
39 |
PD |
40 |
|
|
21 |
41 |
PD |
42 |
|
|
22 |
43 |
PD |
44 |
|
|
23 |
45 |
PD |
46 |
|
|
24 |
47 |
PD |
48 |
|
|
25 |
49 |
PD |
50 |
|
|
26 |
51 |
PD |
52 |
|
|
27 |
53 |
PD |
54 |
|
|
28 |
55 |
PD |
56 |
|
|
29 |
57 |
PD |
58 |
|
|
30 |
59 |
PD |
60 |
|
|
31 |
61 |
PD |
62 |
|
|
32 |
63 |
PD |
64 |
|
|
33 |
PD |
65 |
66 |
Delay=16 |
|
34 |
PD |
67 |
68 |
|
|
35 |
PD |
69 |
70 |
|
|
36 |
PD |
71 |
72 |
|
|
37 |
PD |
73 |
74 |
|
|
38 |
PD |
75 |
76 |
|
|
39 |
PD |
77 |
78 |
|
|
40 |
PD |
79 |
80 |
|
|
41 |
PD |
81 |
82 |
|
|
42 |
PD |
83 |
84 |
|
|
43 |
PD |
85 |
86 |
|
|
44 |
PD |
87 |
88 |
|
|
45 |
PD |
89 |
90 |
|
|
46 |
PD |
91 |
92 |
|
|
47 |
PD |
93 |
94 |
|
|
48 |
PD |
95 |
96 |
To create such RAID 5,
| 1 | Click the Create virtual volume sets or RAIDs button and select Create Virtual Block RAID & Autodetect |
or select Create Virtual Block RAID & Autodetect on the Create menu
Check that the Apply changes immediately check box is clear on the Parents tab. This will prevent R-Studio from trying to start processing the RAID configuration until you specify it completely.
| 2 | Drug the required objects from the Drives pane to the Parents tab and select RAID 5 on the RAID type |
 Other ways to add objects
Other ways to add objects
|
• Control-click the Parents tab and select the required partition from the contextual menu , or • Control-click the partition on the Drives panel, select Add to RAID on the contextual menu, and select the RAID object you want to add the partition to. |
These objects may be hard drives, logical disks, or images . Check that the objects are correctly placed.
Note: Objects should be placed in the same order as they were in the original RAID 5. If this order is incorrect, you must change it by dragging the parents to place them in the correct order.
Object control buttons
|
Locate |
Click this button to locate the selected object in the Drives panel. |
|
Add Empty Space/Add Missing Disk |
Click this button to add an empty space or missing disk object to the RAID |
|
Remove |
Click this button to remove the selected object from the RAID |
|
Move Up |
Click this button to move up the selected object in the RAID |
|
Move Down |
Click this button to move down the selected object in the RAID |
|
Synchronize Offsets |
Click this button to make the offsets the same for all objects in the RAID |
|
Reset changes |
Click this button to return the configuration to the initial state (after clicking the Apply button or immediately after loading) |
| 3 | Specify the Block size and Offset parameters on the Parents tab |
Disregard the Block order field.
| 4 | Specify the parity delay number in the Parity delay control on the Parents tab. |
The number of rows will change to 48.
|
By default, this parameter is set equal to Parity delay . By changing it, you may "shift" the block order table. For example, when the First parity parameter is set as 1 for the RAID 5 of 3 disks with Parity delay of 3., the block order table will be the following:
|
| 5 | Select Left Asynchronous (Continuous) on the Block Order Field and click the Apply button on the Parents tab |
| > | The created Virtual Block RAID 1 object can now be processed like regular drives/volumes |
If R-Studio detects a valid file system on this RAID object, a partition object will appear on the Drives panel.
The Description Files for RAID Configurations topic shows the RAID description file for this RAID configuration.
You also may check the RAID consistency, if necessary. See the Checking RAID Consistency help page for details.
- R-Studio Technician: activation using a USB stick
- Data Recovery Guide
- Why R-Studio?
- R-Studio for Forensic and Data Recovery Business
- R-STUDIO Review on TopTenReviews
- File Recovery Specifics for SSD devices
- How to recover data from NVMe devices
- Predicting Success of Common Data Recovery Cases
- Recovery of Overwritten Data
- Emergency File Recovery Using R-Studio Emergency
- RAID Recovery Presentation
- R-Studio: Data recovery from a non-functional computer
- File Recovery from a Computer that Won't Boot
- Clone Disks Before File Recovery
- HD Video Recovery from SD cards
- File Recovery from an Unbootable Mac Computer
- The best way to recover files from a Mac system disk
- Data Recovery from an Encrypted Linux Disk after a System Crash
- Data Recovery from Apple Disk Images (.DMG files)
- File Recovery after Re-installing Windows
- R-Studio: Data Recovery over Network
- How To Use R-Studio Corporate Package
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted NTFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an ReFS disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted exFAT/FAT Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased HFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased APFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted Ext2/3/4FS Disk
- Data Recovery from an XFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Simple NAS
- How to connect virtual RAID and LVM/LDM volumes to the operating system
- Specifics of File Recovery After a Quick Format
- Data Recovery After Partition Manager Crash
- File Recovery vs. File Repair
- Data Recovery from Virtual Machines
- How to Recover Files from a Remote Computer Using R-Studio Standalone License and Its Network Capabilities in Demo Mode
- How to Connect Disks to a Computer
- Emergency Data Recovery over Network
- Data Recovery over the Internet
- Creating a Custom Known File Type for R-Studio
- Finding RAID parameters
- Recovering Partitions on a Damaged Disk
- NAT and Firewall Traversal for Remote Data Recovery
- Data Recovery from an External Disk with a Damaged File System
- File Recovery Basics
- Default Parameters of Software Stripe Sets (RAID 0) in Mac OS X
- Data Recovery from Virtual Hard Disk (VHD/VHDX) Files
- Data Recovery from Various File Container Formats and Encrypted Disks
- Automatic RAID Parameter Detection
- IntelligentScan Data Recovery Technology
- Multi-pass imaging in R-Studio
- Runtime Imaging in R-Studio
- Linear Imaging vs Runtime Imaging vs Multi-Pass Imaging
- USB Stabilizer Tech for unstable USB devices
- Joint work of R-Studio and PC-3000 UDMA hardware
- Joint work of R-Studio and HDDSuperClone
- R-Studio T80+ - A Professional Data Recovery and Forensic Solution for Small Business and Individuals Just for 1 USD/day
- Backup Articles
- R-Drive Image Standalone and Corporate license transferring
- Fixing Windows update error 0x80070643 with R-Drive Image
- Backup with Confidence
- R-Drive Image as a free powerful partition manager
- Computer Recovery and System Restore
- Disk Cloning and Mass System Deployment
- Accessing Individual Files or Folders on a Backed Up Disk Image
- R-Drive Image startup / bootable version
- File Backup for Personal Computers and Laptops of Home and Self-Employed Users
- Creating a Data Consistent, Space Efficient Data Backup Plan for a Small Business Server
- How to Move the Already Installed Windows from an Old HDD to a New SSD Device and Create a Hybrid Data Storage System
- How to Move an Installed Windows to a Larger Disk
- How to Move a BitLocker-Encrypted System Disk to a New Storage Device
- How to backup and restore disks on Linux and Mac computers using R-Drive Image
- R-Drive Image and Virtual Machines
- Undelete Articles
- Get Deleted Files Back
- Free Recovery from SD and Memory cards
- R-Undelete: Video Recovery
- Recovery from an External Device with a Damaged File System
- File recovery from a non-functional computer
- Free File Recovery from an Android Phone Memory Card
- Free Photo and Video File Recovery Tutorial
- Easy file recovery in three steps