- Contents
- Index
- A -
- B -
Bad Sectors settings
Broken File Name
Rename and change all invalid symbols to:
Broken File Name options
Button
Buttons
- C -
Contact information and technical support
Context menu
Delete All Scanned Information
Find Previous Versions of the File
Find Template Signature Previous
Create menu
- D -
Data Copy in Text/hexadecimal viewer
Dialog boxes
Drive menu
- E -
Edit menu
Find Template Signature Previous
Exclusive Region options
- F -
File Already Exists
File mask options
File menu
File Systems settings
Default encoding for Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 volumes
File Types
Find options
Finding Previous File Versions
- H -
Help menu
- I -
Image options
Compressed image (R-Drive Image compatible)
- K -
Known File Types
- L -
Log settings
Maximum messages in the Event Log
- M -
Main settings
Messages
Double-click a logical disk...
- O -
Opening several disks/partitions in one tab
- P -
Panels
Panes
Properties tab
- R -
Recover options
Condense successful restoration events
Do not recover duplicate files from Extra Found Files
Open local folder (folders) when done
Recover alternative data streams
Recover real folders structure
Region options
- S -
Scan options
Search options
Settings
- T -
Tabs
Technical Information and Troubleshooting
Tools menu
- V -
Various Disk and Volume Managers
View menu
R-Linux Settings
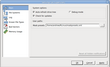
You may specify some global setting for R-Linux on the Settings dialog box. You may reach it by selecting Settings on the Tools menu.
Main
|
System Options |
|
|
Auto-refresh Drive Tree |
If this box is selected, R-Linux automatically refreshes the list of connected disks. You may disable it if R-Linux experiences problems with connected devices. |
|
Debug Mode |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux displays an additional command Create FS Snapshot on the shortcut menu for an object with a file system. An FS Snapshot contains system data for the file system only (file descriptions without file contents). If a problem appears, this snapshot can be sent to R-Linux technical support to identify the problem. This option greatly slows R-Linux . |
|
Check for update |
If this box is selected, R-Linux will automatically check for updates. |
|
User path. Mask presets |
Specifies a file name and path to the file with file mask presets.i |
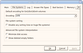
File Systems
|
Default encoding for Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 volumes |
Select the national encoding for the Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 partitions. |
|
Disable any sorting |
Select this option if the number of files on the disk is so large that R-Linux sorts files in selected folders for too long time. |
|
Minimize disk access |
Select this option if a lot of bad sectors are on the hard drive. R-Linux will reduce access to internal files in the file system to speed up the interpretation of file system data. |
|
Show deleted empty folders |
Select this option if you want to view empty deleted folders. |
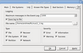
Log
 Log options
Log options
|
Logging |
|
|
Maximum messages in the Event Log |
Specifies the maximum number of messages R-Linux will keep in the event log |
|
Save log to file |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux writes its log into a log file specified in the File name field. |
|
File name |
Specifies the file name in which the log will be saved. |
|
Type |
|
|
File |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux logs all events with recovered files. |
|
File System |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux logs all events with the file system. |
|
Partition |
If this check box selected, R-Linux logs all events with partitions. |
|
Recover |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux logs all events with the recovering processes. |
|
Disk |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux logs all events with disks. |
|
Network |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux logs all events with network operation. |
|
Severity |
|
|
Error |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux adds error messages into its log. |
|
Warning |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux adds warning messages into its log. |
|
Information |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux adds information messages into its log. |
|
Success |
If this check box is selected, R-Linux adds success messages into its log. |
|
NEVER WRITE A LOG FILE ON THE DISK FROM WHICH YOU RECOVER DATA!!! Or you may obtain unpredictable results and lose all your data. |
|
|
Note: If in the Recover dialog box the Condense successful restoration events check box is selected, the Log will display only Error , Warning , and Information event messages. |
|
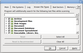
Known File Types
You may specify which Known File Types will be enabled/disabled by default. You may also specify know file types to search for during a specific scan session on the Scan dialog box.
|
Reset |
Click this button to reset the settings to the previous state. Active until the Apply button is clicked. |
|
Select All |
Click this button to select all file types in the list. |
|
Clear All |
Click this button to clear all file types in the list except some predefined ones. |
|
Reset to Recommended |
Click this button to reset the settings to the recommended set. |
Bad Sectors
|
Default read retries count |
Specifies a default value for I/O Tries , or how many times R-Linux will try to read a bad sector. You may specify this parameter for each drive separately on the Properties tab. R-Linux treats bad sectors in the following way: It reads a certain part of disk (predefined by Windows) and • If Default read retries is set to 0, the entire part with bad sectors will be filled with the specified pattern. • If Default read retries is set to a non-zero value, R-Linux reads again that part sector by sector, repeating the attempts the specified number of times. If R-Linux still cannot read a bad sector, it fills the sectors with the specified pattern. In this case only the bad sectors will be filled with the pattern, but that extremely slows the disk read process. For example, if you set Default read attempts to 1, a bad sector will be read 2 times. |
|
Set for all drives |
Click this button to reset I/O Tries for all drives to the default value. |
|
Pattern to fill bad blocks |
Specifies a default pattern R-Linux will use to fill bad sectors in files to recover, in images, or when showing data in the Text/Hexadecimal Viewer . You may specify the pattern either in the ANSI or Hex data format. Note: R-Linux will never ever try to write anything on the disk from which data is to recover or an image is to create. |
Memory Usage
These settings control how much memory R-Linux uses for its work. They help preventing R-Linux from locking when trying to perform very memory-consuming tasks like scanning large disks or processing file systems with a lot of files.
|
Disable memory control |
If this option is selected, the memory control is disabled. |
|
Limit usage of the process memory by |
If this option is selected, R-Linux will automatically stop performing the task when the amount of used virtual memory reaches the specified value. |
|
Limit usage of the process memory by |
If this option is selected, R-Linux will automatically stop performing the task when the amount of used physical memory reaches the specified value. |
You may see how much memory R-Linux actually uses on the Memory Usage dialog box.
- R-Studio Technician: activation using a USB stick
- Data Recovery Guide
- Why R-Studio?
- R-Studio for Forensic and Data Recovery Business
- R-STUDIO Review on TopTenReviews
- File Recovery Specifics for SSD devices
- How to recover data from NVMe devices
- Predicting Success of Common Data Recovery Cases
- Recovery of Overwritten Data
- Emergency File Recovery Using R-Studio Emergency
- RAID Recovery Presentation
- R-Studio: Data recovery from a non-functional computer
- File Recovery from a Computer that Won't Boot
- Clone Disks Before File Recovery
- HD Video Recovery from SD cards
- File Recovery from an Unbootable Mac Computer
- The best way to recover files from a Mac system disk
- Data Recovery from an Encrypted Linux Disk after a System Crash
- Data Recovery from Apple Disk Images (.DMG files)
- File Recovery after Re-installing Windows
- R-Studio: Data Recovery over Network
- How To Use R-Studio Corporate Package
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted NTFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an ReFS disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted exFAT/FAT Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased HFS Disk
- Data Recovery from an Erased APFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Re-Formatted Ext2/3/4FS Disk
- Data Recovery from an XFS Disk
- Data Recovery from a Simple NAS
- How to connect virtual RAID and LVM/LDM volumes to the operating system
- Specifics of File Recovery After a Quick Format
- Data Recovery After Partition Manager Crash
- File Recovery vs. File Repair
- Data Recovery from Virtual Machines
- How to Recover Files from a Remote Computer Using R-Studio Standalone License and Its Network Capabilities in Demo Mode
- How to Connect Disks to a Computer
- Emergency Data Recovery over Network
- Data Recovery over the Internet
- Creating a Custom Known File Type for R-Studio
- Finding RAID parameters
- Recovering Partitions on a Damaged Disk
- NAT and Firewall Traversal for Remote Data Recovery
- Data Recovery from an External Disk with a Damaged File System
- File Recovery Basics
- Default Parameters of Software Stripe Sets (RAID 0) in Mac OS X
- Data Recovery from Virtual Hard Disk (VHD/VHDX) Files
- Data Recovery from Various File Container Formats and Encrypted Disks
- Automatic RAID Parameter Detection
- IntelligentScan Data Recovery Technology
- Multi-pass imaging in R-Studio
- Runtime Imaging in R-Studio
- Linear Imaging vs Runtime Imaging vs Multi-Pass Imaging
- USB Stabilizer Tech for unstable USB devices
- Joint work of R-Studio and PC-3000 UDMA hardware
- Joint work of R-Studio and HDDSuperClone
- R-Studio T80+ - A Professional Data Recovery and Forensic Solution for Small Business and Individuals Just for 1 USD/day
- Backup Articles
- R-Drive Image Standalone and Corporate license transferring
- Fixing Windows update error 0x80070643 with R-Drive Image
- Backup with Confidence
- R-Drive Image as a free powerful partition manager
- Computer Recovery and System Restore
- Disk Cloning and Mass System Deployment
- Accessing Individual Files or Folders on a Backed Up Disk Image
- R-Drive Image startup / bootable version
- File Backup for Personal Computers and Laptops of Home and Self-Employed Users
- Creating a Data Consistent, Space Efficient Data Backup Plan for a Small Business Server
- How to Move the Already Installed Windows from an Old HDD to a New SSD Device and Create a Hybrid Data Storage System
- How to Move an Installed Windows to a Larger Disk
- How to Move a BitLocker-Encrypted System Disk to a New Storage Device
- How to backup and restore disks on Linux and Mac computers using R-Drive Image
- R-Drive Image and Virtual Machines
- Undelete Articles
- Get Deleted Files Back
- Free Recovery from SD and Memory cards
- R-Undelete: Video Recovery
- Recovery from an External Device with a Damaged File System
- File recovery from a non-functional computer
- Free File Recovery from an Android Phone Memory Card
- Free Photo and Video File Recovery Tutorial
- Easy file recovery in three steps